
KEYTAKEAWAYS
- The Graph acts as the “Google of blockchains,” enabling developers to query structured on-chain data efficiently across dApps and multi-chain ecosystems.
- GRT serves as the core utility token, coordinating indexers, curators, delegators, and consumers while ensuring network security, incentives, and governance.
- With adoption from Uniswap, AAVE, and thousands of dApps, The Graph continues to expand, driving long-term value growth for the GRT token.

CONTENT
The Graph is a decentralized indexing protocol powering Web3 data access. Learn how GRT secures, incentivizes, and scales blockchain queries across leading dApps and multi-chain ecosystems.

WHAT IS THE GRAPH?
The Graph was founded in 2018 by Yaniv Tal, Jannis Pohlmann, and Brandon Ramirez, who had already been collaborating on developer-focused tools.
Since 2019, the project has raised over $195 million in funding, including a $10 million public sale in October 2020. In its early token distribution, 100 million GRT were allocated, with 21% going to investors such as Coinbase Ventures, Digital Currency Group, and Multicoin Capital. These early backers laid a strong foundation for The Graph’s growth and adoption.

📌 Introduction to The Graph
As the blockchain industry expands rapidly, the demand for reliable on-chain data has surged. However, blockchain’s decentralized design makes querying information less efficient than centralized databases, often resulting in high gas costs.
The Graph addresses this problem as a decentralized indexing protocol. By leveraging a system similar to IPFS crawling, it organizes and stores blockchain data so developers can query it efficiently. Instead of general users, the main audience is developers who need accurate, real-time access to blockchain data for their decentralized applications (dApps). In simple terms, if Google is the search engine of the internet, then The Graph can be seen as the search engine of blockchains.
The protocol is already widely used across leading dApps such as Uniswap, Synthetix, Aragon, AAVE, Gnosis, Balancer, Livepeer, DAOstack, and Decentraland, with more than 3,000 subgraphs deployed. Anyone can contribute to building or indexing these subgraphs, making it a fully decentralized ecosystem. In practice, The Graph functions like a decentralized version of Etherscan or BscScan, allowing structured blockchain data to be indexed and queried seamlessly.
What is The Graph? pic.twitter.com/otTd8rsn2S
— The Graph (@graphprotocol) December 11, 2024
📌 Revenue Model of The Graph
According to Messari, The Graph’s revenue primarily comes from two streams:
- Query fees paid by consumers accessing blockchain data
- Inflationary rewards distributed through the protocol
Since its mainnet launch in 2021, The Graph has expanded to support data indexing across 26 different networks, including Ethereum, NEAR, Arbitrum, Optimism, Polygon, Avalanche, Celo, Fantom, Moonbeam, and IPFS. With the ongoing rise of multi-chain ecosystems, The Graph has solidified its role as a critical layer of Web3 infrastructure, powering data accessibility and scalability for developers worldwide.
>>> More to read: What is MYX Finance & $MYX?
THE GRAPH STRENGTHS & WEAKNESSES
✅ Strengths
-
Supports GraphQL APIs – Developers can query data efficiently from the front end and access comprehensive results in a single request.
- Fully decentralized service – The Graph aims for 100% decentralization, though some engineering work is still ongoing.
- Adopted by leading DeFi protocols – Many projects, including Synthetix, Uniswap, Aragon, and Decentraland, already rely on The Graph for production-level applications.
❗ Weaknesses
- Early-stage project – Although backed by venture capital, The Graph is still in its early phases and continues to mature.
- Steep learning curve – Developers must be familiar with WebAssembly, making the onboarding process more technically demanding compared to traditional solutions.
>>> More to read: What is Linea (LINEA)? A Complete Guide
WHAT IS GRT?
Staying true to the spirit of decentralization, The Graph introduced the GRT token to ensure long-term sustainability and active participation across its ecosystem. GRT is an ERC-20 token built on Ethereum and serves as the core utility and governance token of the protocol.
🪙 Utility of GRT
GRT is essential for coordinating the work between indexers, curators, delegators, and consumers within The Graph network. It allows participants to stake tokens in order to provide or access data, ensuring the network’s economic security and data integrity.
- Indexers stake GRT to provide indexing services and earn query fees.
- Curators signal on subgraphs by staking GRT, guiding indexers toward valuable data sources.
- Delegators stake GRT by delegating to indexers, securing the network while earning a portion of rewards.
- Consumers pay in GRT for queries and data retrieval, ensuring a direct link between network usage and token utility.
Through this structure, GRT creates an incentive-driven marketplace that aligns accuracy, efficiency, and reliability across the network.
🪙 Tokenomics of GRT
The total supply of GRT is capped at 10 billion tokens. When The Graph officially launched in October 2020, 4.2% of the supply was sold to the public. The distribution was designed to balance early adopters, network participants, and long-term development needs:
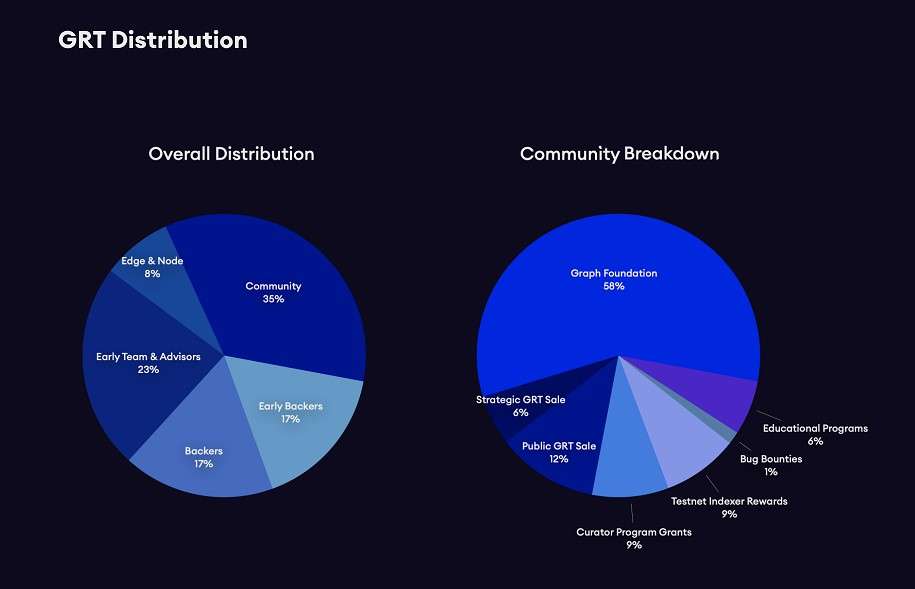
- 3.15% allocated to early adopters and testnet participants.
- 3.15% reserved as incentives for curators signaling high-quality subgraphs.
- 34% allocated to early backers and supporters.
- 23% distributed to the team and advisors, vesting over time.
- 6.3% sold in public sales, including 4.2% at launch and 2.1% to the community.
- 8% allocated to support ecosystem growth and development.
- 12% used for educational initiatives and building developer communities.
- 2.5% reserved for bug bounties and community security programs.
- 0.5% allocated to advisory partners.
- 20% reserved for the Graph Foundation, ensuring sufficient funding to safeguard and upgrade the protocol.
THE GRAPH CONCLUSION
Overall, the value of the GRT token is closely tied to the growth of blockchain and the DeFi ecosystem, while also depending heavily on the expansion of its own services. In recent years, The Graph Network has grown rapidly, and key factors influencing GRT include how frequently users query its APIs and whether the user base continues to expand.
From the perspective of adoption, as more dApps and digital assets integrate The Graph Network into their platforms, overall usage has steadily increased. At the same time, the protocol has been broadening its scope, creating additional growth opportunities for developers and users alike. This suggests that, over the long run, The Graph Network is positioned to sustain growth and further enhance the value of the GRT token.
For traders and investors, it is critical to monitor whether The Graph Network can continue to scale and whether user demand will persist. At the same time, shifts in the broader blockchain and DeFi markets must also be considered, as GRT remains tightly connected to these macro developments.
In short, understanding how these dynamics shape the GRT token’s performance can help investors make smarter, more informed decisions in navigating the evolving crypto landscape.

















