KEYTAKEAWAYS

CONTENT
‘Bear Market’ is often synonymous with economic downturns and can signal the beginning of a decline in investment profits. It’s a phrase that can strike fear into the hearts of many investors. In this article, we will explore the causes of bear markets and delve into the history of crypto bear markets. Most importantly, we will provide readers with investment strategies to consider during a crypto bear market so that they can maximize their profits even in the midst of challenging times.
WHAT IS A BEAR MARKET?
The bear market is primarily defined as a sustained decline in market prices or performance, typically with a fall of more than 20% in a long-term trend. Bear markets are often accompanied by a pessimistic attitude among global investors, a significant sell-off of investment products, and a downturn in the overall economic environment.
Financial indicators can also help us determine whether the market has entered a bear market by examining various key economic data. Here are a few indicative metrics for readers to consider when assessing whether the market has turned bearish:
- Disposable Income
Disposable income refers to the income remaining after non-consumption expenses have been deducted, which can be used to cover daily living expenses (consumption expenses). During an economic downturn, the disposable income of the public tends to decrease.
- Unemployment Rate
The job market has always been closely related to economic trends. In the past, when the economy experienced a recession or major crisis, the unemployment rate would noticeably rise. For example, during the economic crisis of 1979 in the United States, the unemployment rate increased significantly. The two recent crises of the 2008 financial crisis and the 2019 COVID-19 pandemic also saw rapid increases in unemployment rates.
- Corporate Profits
During a bear market, when the economy is sluggish, corporate performance is also affected, with most companies’ revenues declining.
- Productivity
Following corporate profits, productivity also tends to decline during a bear market (or economic recession).
- More to Read about Crypto Bull Market
CRYPTO BEAR MARKET HISTORY
In fact, the crypto bear market happens in the crypto world as well. Although one of the cryptos’ characteristics is rapid and drastic price fluctuations, a review of their history since their inception reveals several prolonged periods of low prices.
Below, we will provide detailed introductions to these crypto bear markets and explain the reasons behind them:
- 2013 Crypto Bear Market
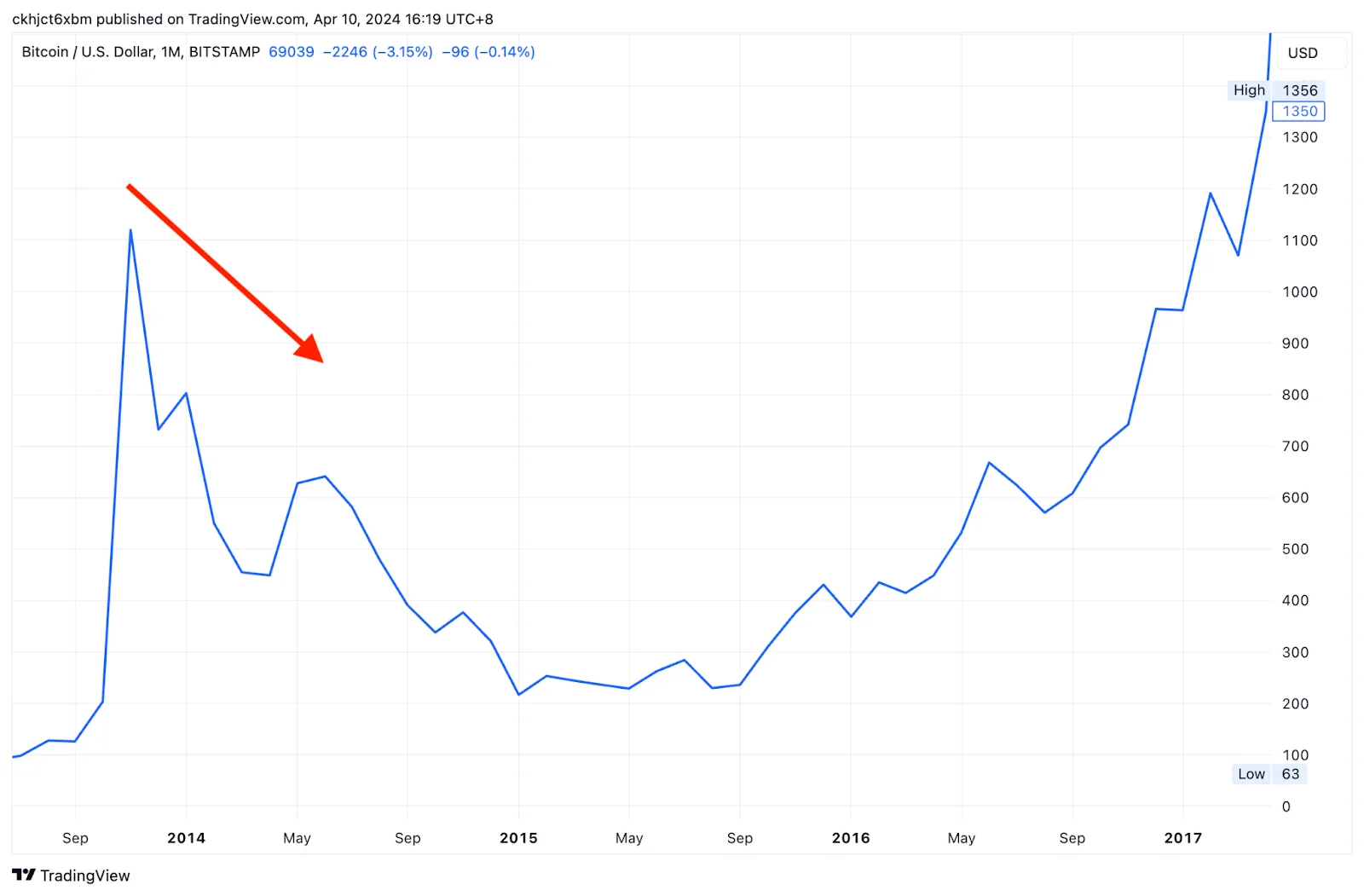
In November 2013, Bitcoin experienced a surge, rising from $200 to a historical high of $1,129 within a month. The primary reason was the recognition of Bitcoin as legal tender in European countries, coupled with the influx of Asian investors, making Bitcoin a hot investment topic at that time.
However, after the surge, there was often a sharp decline. Bitcoin began its first major crash in December, falling to a low of $178 per BTC by January 2015. This became the largest crash in Bitcoin’s history.
The reason for Bitcoin’s first crash and crypto bear market is panic selling after a bull market.
Crypto assets emphasize decentralization, so significant fluctuations are common, and the reasons for sharp rises and falls are not easy to explain in a few words. One potential reason for the situation around 2013 could be the Chinese government’s issuance of the “Notice on Preventing Bitcoin Risks,” which caused rumors to spread in the market, leading to panic selling.
- 2017 Crypto Bear Market
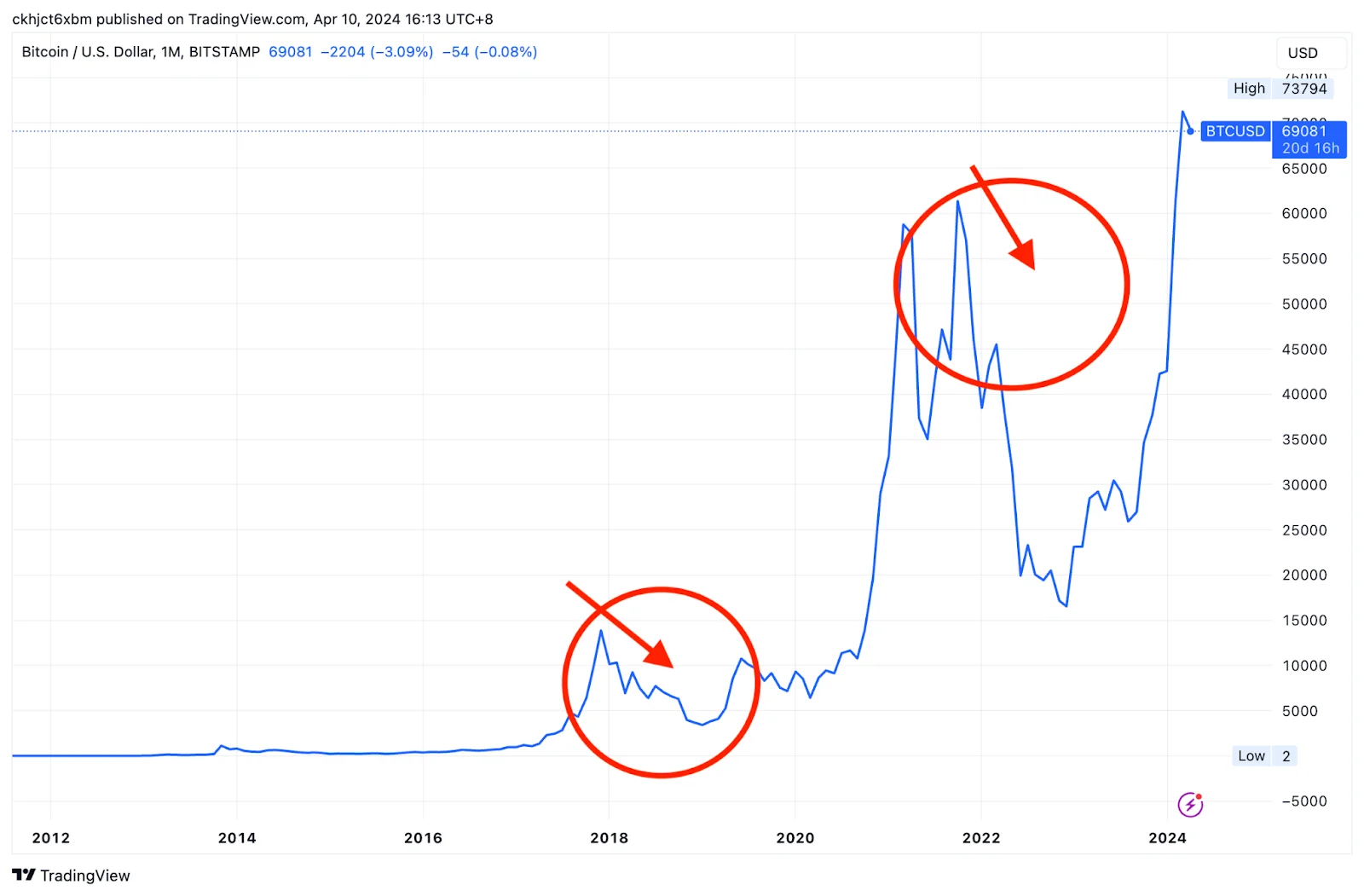
The second Bitcoin crash in 2017 brought the longest crypto bear market to date. At that time, Bitcoin fell from $19,900 at the end of 2017 to $6,955 by the beginning of February 2018, with the price dropping by more than half.
Although there were signs of a rebound afterward, the price never returned to its previous high and continued to explore new lows, reaching around $3,800 in early 2019 and only beginning to recover in mid to late 2019.
The reason for Bitcoin’s second crash and crypto bear market was that various unfavorable market news appeared simultaneously.
To this day, the Bitcoin crash of 2017 remains a topic of discussion in the crypto market, with the underlying reasons often compared with subsequent crashes. This includes governments starting to regulate cryptos, the collapse of popular derivatives like futures, and panic selling after a sharp rise, with various reasons appearing simultaneously and no positive news to stimulate the market, leading to continuous selling.
- 2021 Crypto Bear Market
Bitcoin’s price rose rapidly in late 2019, reaching a new high in 2021. This increase was more significant than previous ones, with the price jumping from around $10,000 to $40,000, then reaching a recent high of $63,000 in April 2021, before falling back to $29,807 in July, with the price evaporating by more than half.
The reason for the 2021 crypto bear market is a crisis of confidence in the new crypto ecosystem.
Some say that Bitcoin’s rapid stabilization of price after this decline does not constitute a ‘crash’ or ‘crypto bear market.’
However, the situation in 2021 was slightly different from previous times. Firstly, major public chain tokens such as AVAX, SOL, and LUNA were launched, while NFTs and GameFi rapidly emerged, and the functionality of liquidity mining/staking became increasingly sophisticated. The crypto ecosystem was no longer comparable to that of 2017 or 20132, and Bitcoin, as the leading crypto token, often reflects the mood of the entire market.
The sharp decline in mid-2021 was seen by many as the first crisis of confidence in this broader environment, so it was once considered another crash.
THE TRADING STRATEGIES DURING THE CRYPTO BEAR MARKET
Looking at the above introductions to traditional financial market bear markets and crypto bear markets, although crypto bear markets imply a pessimistic overall investment market with deteriorating economic performance, this does not mean that investors cannot profit from it. Below, we will introduce two investment strategies that can allow investors to profit or minimize potential losses during a cryptocurrency bear market:
Short Selling
If investors believe that the crypto bear market has not bottomed out and may continue to explore for a while, they can consider short selling to make a profit.
Short selling is the opposite of the familiar strategy of buying low and selling high. It involves investors borrowing certain crypto and selling it at the current market value, then buying it back later at the current price.
If the price of the crypto falls as expected in the future, investors can profit from the price difference.
For example, if the current price of Bitcoin is $70,000, and an investor expects it to fall to $60,000 later, the investor can borrow Bitcoin and sell it at $70,000, then buy it back when the price really falls to $60,000. This operation can bring the investor a profit of $10,000.
- More to Read about Oher Crypto Trading Strategies for Beginners
Diversification
If investors are worried about subsequent price declines causing too much loss in the crypto bear market, they can consider diversifying their assets into different cryptocurrencies or even different financial products to reduce the risk of loss. The recent Bitcoin spot ETF, with its lower volatility, does not need to worry about experiencing drastic price changes like spot trading, and is also an investment option for investors to consider. Buying into the ETF when it reaches a low price and waiting for the cryptocurrency market to warm up can yield profits.
- More to Read about Asset Allocation
CONCLUSION
Defined by a sustained decline exceeding 20%, bear markets are marked by shrinking disposable income, rising unemployment rates, declining corporate profits, and reduced productivity. The crypto market, despite its rapid price fluctuations, is no stranger to bear markets, with significant crashes in 2013, 2017, and 2021 shaking investor confidence and reshaping the landscape. These downturns are often triggered by regulatory fears, market saturation, and panic selling. However, even in the depths of a crypto bear market, investors can still seize opportunities to gain profit. Strategies like short selling and diversification offer chances for profit or loss mitigation.
As the crypto ecosystem continues to evolve, with new technologies and platforms reshaping the market, a crypto bear market is likely to occur at any time ( even if the crypto market seems optimistic now, we can’t entirely deny the possibility of the crypto bear market 2024). Investors should keep an eye on the trend and manage the risk of investment carefully.
FAQ
- What is a bear market?
A: The bear market is usually described as a sustained decline in market prices, normally with a fall of more than 20% in a long-term trend.
- Does the crypto bear market exist?
A: Yes, even crypto bear markets happened in 2013, 2017, and 2023, respectively. Even though cryptos are known for their rapid and drastic price fluctuations, there have been several prolonged periods of low prices.
- What are the trading strategies during the crypto bear market?
A: Investors can minimize risks and losses, and maximize their profits during crypto bear markets via short selling and diversification.
Looking for the latest scoop and cool insights from CoinRank? Hit up our Twitter and stay in the loop with all our fresh stories!















